Effective Ways to Issue a 1099 in 2025: Essential Steps for Tax Compliance
Issuing a 1099 form can seem daunting, but ensuring compliance with IRS guidelines is crucial for businesses and contractors alike. This article presents effective ways on how to issue a 1099 in 2025, detailing the essential steps and practices that ensure seamless execution of your filing obligations. By understanding the 1099 form instructions and IRS 1099 guide, you’ll mitigate errors and align with regulatory requirements.
Understanding the 1099 Form Types
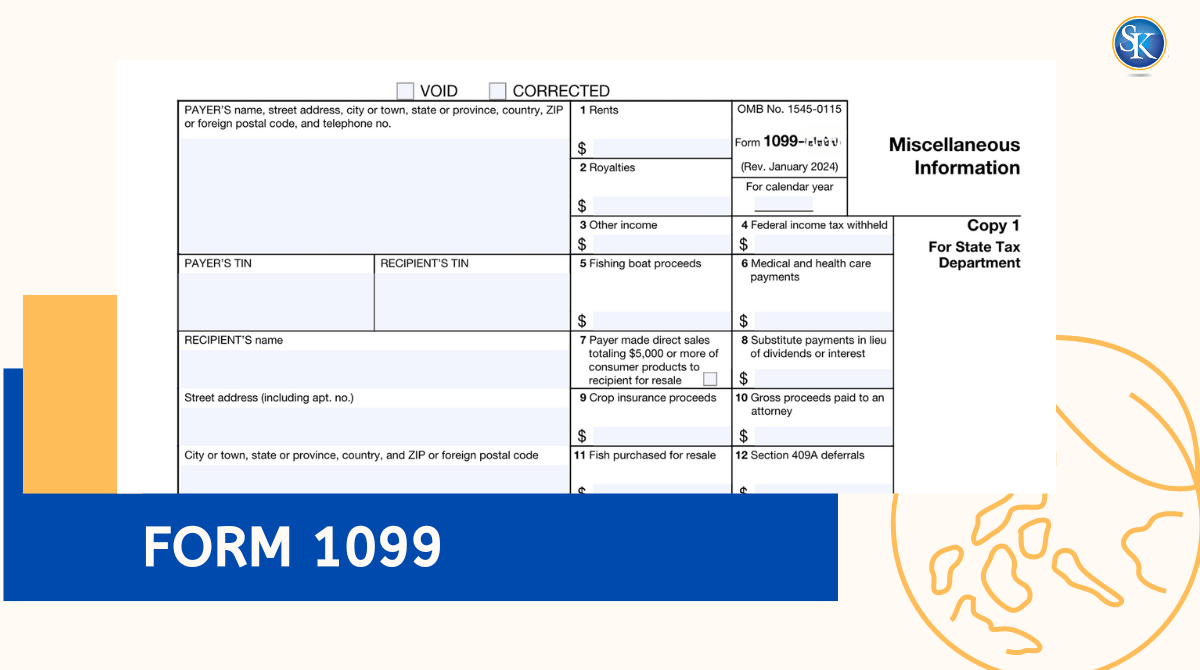
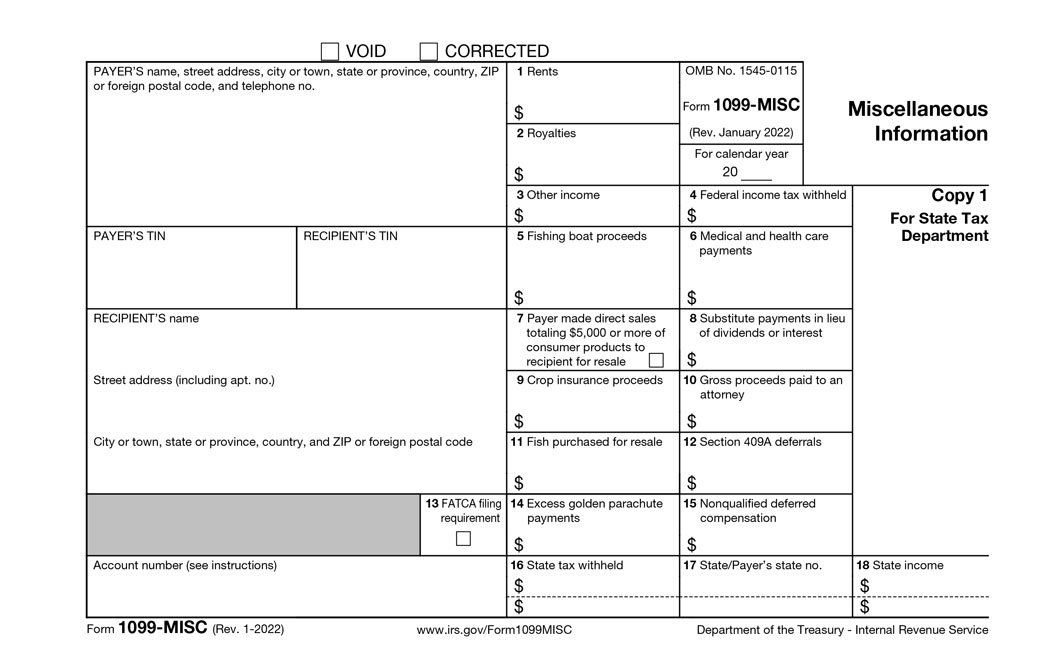
Before diving into the specifics of issuing a 1099, it’s essential to comprehend the various types of 1099 forms available. The most common form, the 1099-NEC, is used to report payments made to non-employees, such as independent contractors. Other forms that may be relevant include the 1099-MISC for miscellaneous income and 1099-DIV for dividends. Each serves a different reporting purpose, making it critical for businesses to categorize their payments correctly based on the 1099 reporting requirements.
The Significance of Different 1099 Forms
Differentiating between various types of 1099 forms is fundamental to ensuring compliance and accurate reporting. For instance, the 1099-NEC is explicitly designated for reporting non-employee compensation exceeding $600 in a tax year. Understanding the distinctions between forms like 1099-MISC, 1099-INT, and others allows businesses to avoid misclassifying income, thus reducing potential penalties or compliance issues with the IRS. Proper usage of these forms can also enhance a business’s credibility and record-keeping practices.
How to Classify Payments Properly
When issuing a 1099, classifying payments rightly is crucial. It ensures that the correct form is filed based on the nature of the payment. For example, payments made to service providers like freelancers necessitate the 1099-NEC form, while payments to landlords typically require the 1099-MISC. Many businesses find it beneficial to maintain a checklist detailing 1099 reporting for businesses to streamline the classification process and ensure no forms are missed when year-end approaches.
Steps to Issue a 1099 Form
Now that we’ve clarified the different 1099 forms, let’s delve into the detailed procedural steps involved in issuing one. Knowing when to issue a 1099 and following a systematic approach helps ensure compliance and helps prevent any costly mistakes or penalties from the IRS.
Gather Necessary Information
The foremost step in issuing a 1099 to contractors is collecting the appropriate information. Businesses must obtain the correct Tax Identification Number (TIN) from all contractors and ensure it is ready before the issuance of the form. This often involves collecting a W-9 form from the contractor, which confirms their identification and compliance with tax filing regulations. Accurate data collection sets the foundation for smooth processing.
Utilize 1099 E-Filing Options
The 1099 e-filing process has gained popularity in recent years due to its efficiency and accuracy. E-filing not only simplifies the submission process but also reduces the likelihood of errors that can occur with paper submissions. To successfully e-file 1099 forms, businesses should choose reliable e-filing service providers that comply with IRS 1099 filing guidelines. This method also generally allows for faster processing and receipt confirmation from the IRS.
1099 Deadlines and Compliance
Understanding 1099 deadlines for submission is a crucial aspect of tax compliance. Failing to meet these deadlines can lead to financial penalties and complicate tax obligations. Knowing the specific deadlines for e-filing and paper filing, along with necessary distribution dates to recipients, keeps businesses accountable and aligned with the IRS.
1099 Submission Deadlines
In 2025, the key deadline for filing a 1099 generally remains the 31st of January for forms filed by paper and the 28th of February for electronic submissions. Businesses must ensure that they are well aware of these timelines and plan ahead to compile the required data and documentation. Setting internal reminders can help prevent any oversight. Early issuance of forms can also safeguard against potential last-minute hurdles.
Implications of Late or Incorrect 1099 Filing
Failure to adhere to the 1099 filing deadlines can lead to substantial penalties. If a business is late in issuing forms or if the forms contain errors such as incorrect TINs, the IRS enforces fines. Ultimately, not only could this lead to additional financial liabilities, but it can also affect a business’s tax deductions. Understanding this can ensure accountability and accuracy in the filing process!
Best Practices for Accurate 1099 Issuance
Implementing best practices plays a vital role in smooth 1099 documentation. By following these strategies, businesses can reduce risks associated with filing errors and IRS audits.
Regular Updates on IRS 1099 Changes
Staying informed on IRS 1099 requirements for the tax year ensures that businesses comply with any changes in filing requirements. For instance, changes to the 1099 form formats, e-filing requirements, or additional reporting guidelines may affect your filing process. Subscribe to IRS updates and ensure your accounting team receives training wherever necessary.
Documenting Everything Properly
Keeping organized records is fundamental in the 1099 distribution process. Maintain clear documentation of payments made, forms issued, and any correspondence with contractors about their payment statuses. With credible documentation, dealing with potential audits becomes less daunting, and justification of your submitted 1099 forms enhances compliance.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the various types of 1099 forms and when to use them.
- Gather all necessary information and utilize e-filing options for faster processing.
- Track 1099 submission deadlines to avoid penalties.
- Adopt best practices like diligent record-keeping and staying updated on IRS guidelines.
FAQ
1. What is the importance of a 1099 form?
The 1099 form is crucial for accurately reporting income to the IRS. It ensures compliance with tax obligations for non-employee compensation, rental income, and various incomes that are otherwise not covered under traditional salary structures. It also allows businesses to document payments made, which can significantly impact financial reporting and tax deductions.
2. How does electronic filing facilitate the 1099 process?
Electronic filing streamlines the 1099 submission process, allowing for quicker processing and immediate confirmation from the IRS. This efficient method reduces the chances of errors associated with manual paper submissions, minimizing the potential penalties and complications that arise from inaccuracies.
3. What are the consequences of not issuing a 1099?
Failing to issue a 1099 can result in fines from the IRS, especially if the amounts reported reach certain thresholds. Non-compliance may also invite audits and scrutiny on a business’s financial documents. Not issuing a 1099 on applicable payments can affect the contractor’s tax situation, leading to issues for both parties involved.
4. Are there penalties for late or incorrect 1099 filings?
Yes, the IRS imposes penalties for both late and incorrect filings, which can range from mild to very hefty, depending on the delay and the extent of the inaccuracies. It’s crucial to be diligent and ensure timely and accurate submissions to prevent these liabilities.
5. Who should receive a 1099 form?
Generally, individuals or businesses that receive $600 or more in non-employee compensation, payments for services, rent, royalties, or other types of income typically receive a 1099. Familiarity with the various **1099 reporting requirements** will enable a better understanding of which recipients to include.
6. Can I correct a 1099 after submission?
Yes, if there are errors on your submitted 1099 forms, you must file a correction using the same type of 1099 form but marking it appropriately as a corrected form. Adhering to specified guidelines issued by the IRS is crucial for rectifying any discrepancies.