Essential Guide to How to Find Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Effectively in 2025
Understanding atomic structure is fundamental to chemistry and physics. This guide will walk you through effective methods for finding protons, neutrons, and electrons, illuminating the intricate connection between them. Whether you’re a student, a teacher, or a passionate science enthusiast, mastering these concepts is crucial for grasping the nature of matter.
Understanding Atomic Structure Basics
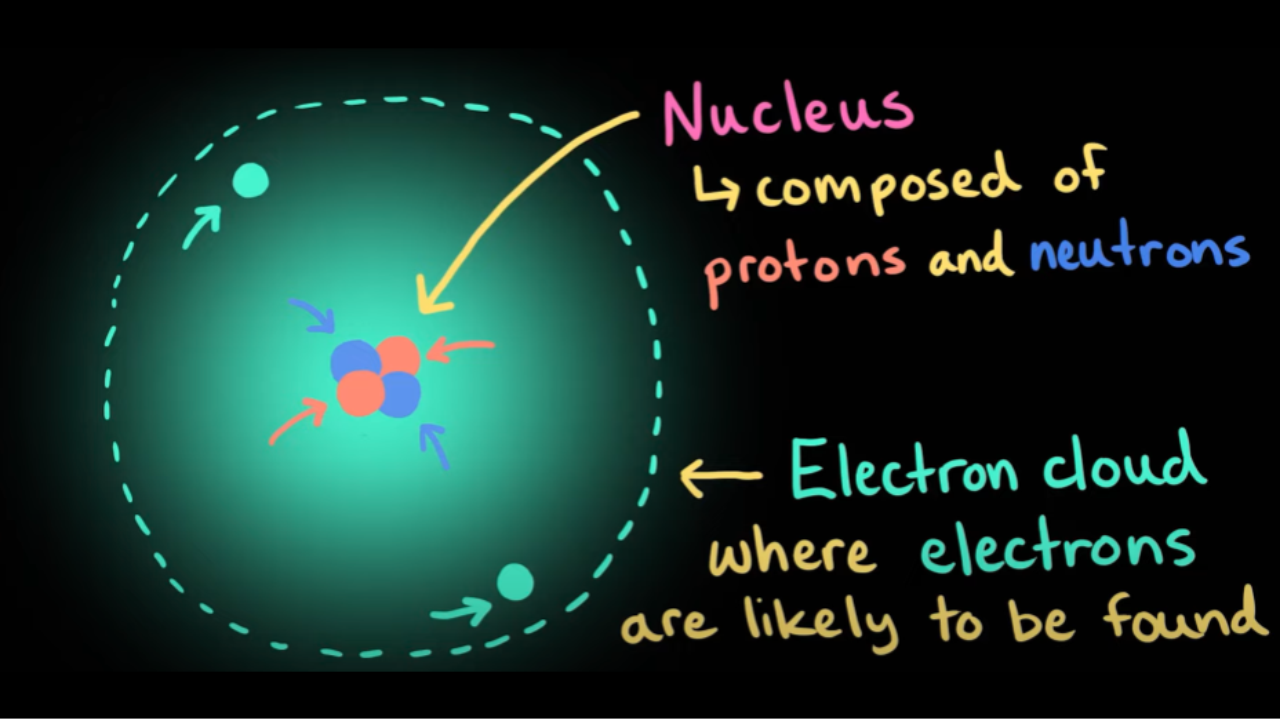
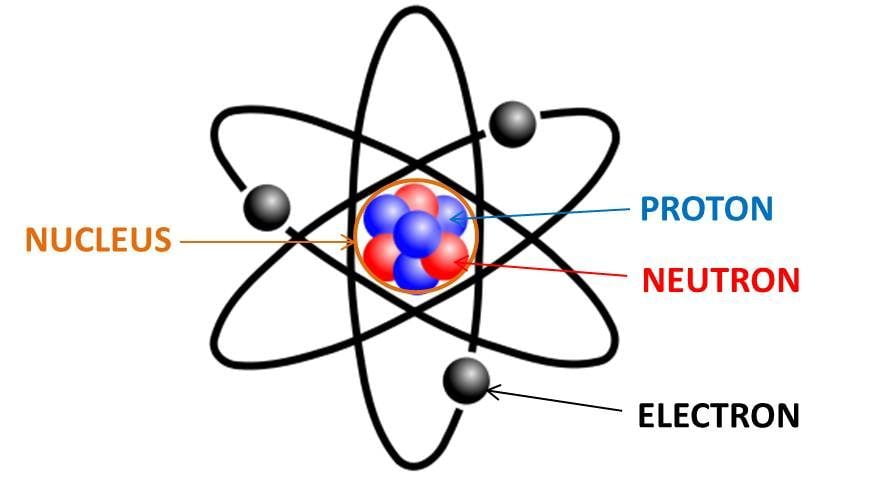
Before diving into how to find protons, neutrons, and electrons, it’s vital to have a solid grasp of atomic structure. Every atom consists of three primary subatomic particles: **protons**, **neutrons**, and **electrons**. Protons carry a positive charge and are found in the nucleus alongside neutrons, which possess no charge (neutral). Electrons, conversely, orbit around the nucleus and hold a negative charge. This balance of charges is crucial for atomic stability and reaction processes.
What Are Protons and Their Role in Atoms?
Protons are positively charged particles located in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons an atom possesses is called its **atomic number**, which uniquely identifies each element on the periodic table. For example, hydrogen has one proton, while helium has two. Understanding the atomic number is vital for finding protons effectively, as it directly corresponds to the element’s identity. In practice, counting the number of protons is straightforward when you reference the periodic table. Simply locate the element, and you’ll find its atomic number indicated at the top of the box.
Defining Neutrons and Their Importance
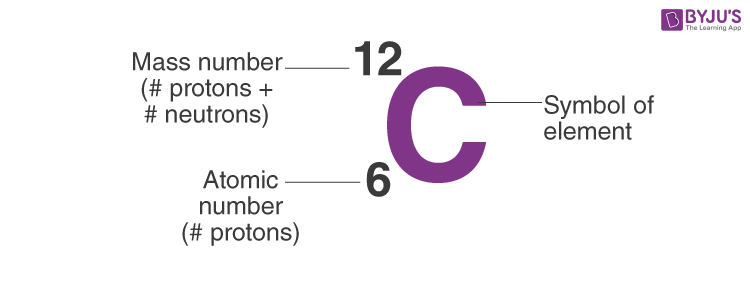
**Neutrons** are electrically neutral particles that vary in number among isotopes of the same element. While the atomic number of an element tells you how many protons it has, the **mass number**, which is the total number of protons and neutrons, is what provides insight into the stability of an atom. To calculate neutrons, subtract the atomic number from the mass number. For instance, if you have a carbon atom with a mass number of 12 and an atomic number of 6, the number of neutrons is 12 – 6 = 6.
Locating Electrons in Atoms
Electrons are essential to an atom’s characteristics, and their arrangement around the nucleus is described by **electron configuration**. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom, which maintains electrical neutrality. Understanding how these particles are distributed helps unravel atomic behavior in chemical reactions.
The Basics of Electron Configuration
Electron configuration is a system that describes how electrons populate the different atomic orbitals. For example, the electron configuration for oxygen (atomic number 8) is 1s² 2s² 2p⁴, which indicates that there are two electrons in the first shell and six in the second, effectively counting how electrons influence atoms and their reactivity. Recognizing patterns in electron arrangements allows chemists to predict how different elements will bond and interact during reactions, highlighting the importance of locating electrons in chemical analysis.
Visualizing the Electron Cloud
To grasp the concept of electron arrangements, it’s beneficial to visualize the *electron cloud*, which represents the likelihood of finding an electron in various regions around the nucleus. This is where the quantum mechanical model comes into play. Instead of definite paths followed by electrons, these clouds signify areas where electrons are likely to be found, which can differ dramatically among different elements.
Calculating Total Proton and Neutron Counts
To effectively acquire an understanding of an atom’s atomic composition, knowing not only how to find protons and neutrons, but also how to calculate their totals, is instrumental. This is particularly essential when working with isotopes or identifying atomic stability factors.
Counting Protons Accurately
Finding total protons in an atom is closely allied to determining the **atomic number** mentioned earlier. Once you reference the periodic table, the top numeral is your answer. However, if you’re working with isotopes, and you need precise quantities for complex analyses, pay close attention to differentiation based not just on atomic mass, but also neutron variation. Thus, **element charge distribution** remains balanced, guaranteeing overall atomic stability.
Efficiently Counting Neutrons
To compute neutrons effectively, the steps are simple: acquire the atomic number and the mass number. Using the example of carbon again, if you know the mass number is 12 and the atomic number is 6, the calculation would yield: 12 (mass number) – 6 (atomic number) = 6 neutrons. This process illustrates how electrons also engage in altering mass numbers among isotopes, spotlighting neutron stability’s role in this balance.
Exploring Relationship Between Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
The relationship between protons, neutrons, and electrons is fundamental to comprehending an atom’s stability and reactivity. Each particle plays a critical role in defining the atomic properties, influencing reactions, and the element’s overall behavior in the periodic context.
Balancing Protons and Electrons
A neutral atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, which cancels their charges. However, when atoms gain or lose electrons, they form ions, resulting in an overall charge distribution that can significantly influence their chemical behavior. Understanding how these particles interact is pivotal in fields such as electrochemistry, influencing how atoms behave during complex reactions.
Protons and Neutrons in Nuclear Reactions
The presence of neutrons adds stability to the nucleus. In nuclear reactions, an imbalance in protons and neutrons can lead to radioactivity, underlined by the principles of **fission and fusion processes**. Consequently, understanding how these particles impact nuclear processes is essential for grasping modern physics and chemistry applications, enhancing the overall elemental analysis throughout scientific disciplines.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding how to find protons, neutrons, and electrons is essential for exploring atomic structure.
- Protons define the atomic number and identity of an element, while neutrons influence its stability.
- Electron configuration reveals the arrangement of electrons, impacting chemical properties and behaviors.
- Relationships among atomic particles drive reactions and nuclear processes, fundamental in chemistry and physics.
FAQ
1. How can I find the total number of protons in an atom?
To find the total number of **protons** in an atom, refer to the periodic table, where the atomic number is displayed prominently. This atomic number corresponds directly to the number of protons in the nucleus, effectively defining the element itself. For example, sodium has an atomic number of 11, meaning it has 11 protons.
2. What is the difference between protons and neutrons?
The primary difference between **protons** and **neutrons** lies in their charge. Protons are positively charged, while neutrons are neutral, carrying no charge. Both are located in the atomic nucleus and contribute to the atom’s mass, yet vary in quantity leading to different isotopes of the same element.
3. How do I determine the number of neutrons in an atom?
To determine
the number of neutrons, subtract the atomic number from the mass number. This calculation provides the total neutrons in the atom. For instance, for carbon with a mass number of 12 and an atomic number of 6, the neutrons would be 12 – 6 = 6 neutrons.
4. What role do electrons play in atomic structure?
**Electrons** play a crucial role in determining an atom’s chemical behavior and bonding. By occupying various energy levels and orbitals, they contribute to the atom’s reactivity and influence how atoms interact during chemical reactions, ultimately defining the element’s properties.
5. Can you explain what mass number signifies?
The **mass number** of an atom signifies the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. This number is essential for understanding isotopes of the same element and how they may differ in stability and reactive properties, fundamental concepts in atomic chemistry.
6. How does the concept of proton-neutron ratios affect stability in atoms?
The **proton-neutron ratio** is critical in determining nuclear stability. When this ratio becomes too high or too low, it can lead to instability and radioactive decay. Understanding this concept is vital in fields like nuclear physics and chemistry.
7. What is electron configuration and why is it important?
**Electron configuration** outlines how electrons are distributed among different atomic orbitals. This configuration affects an atom’s ionization energy, affinity, and overall chemical bonding, making it a core principle in understanding chemical interactions and properties.
By mastering these methods and principles in 2025, you’ll strengthen your grasp of **atomic theory fundamentals** and efficiently analyze the building blocks of matter!