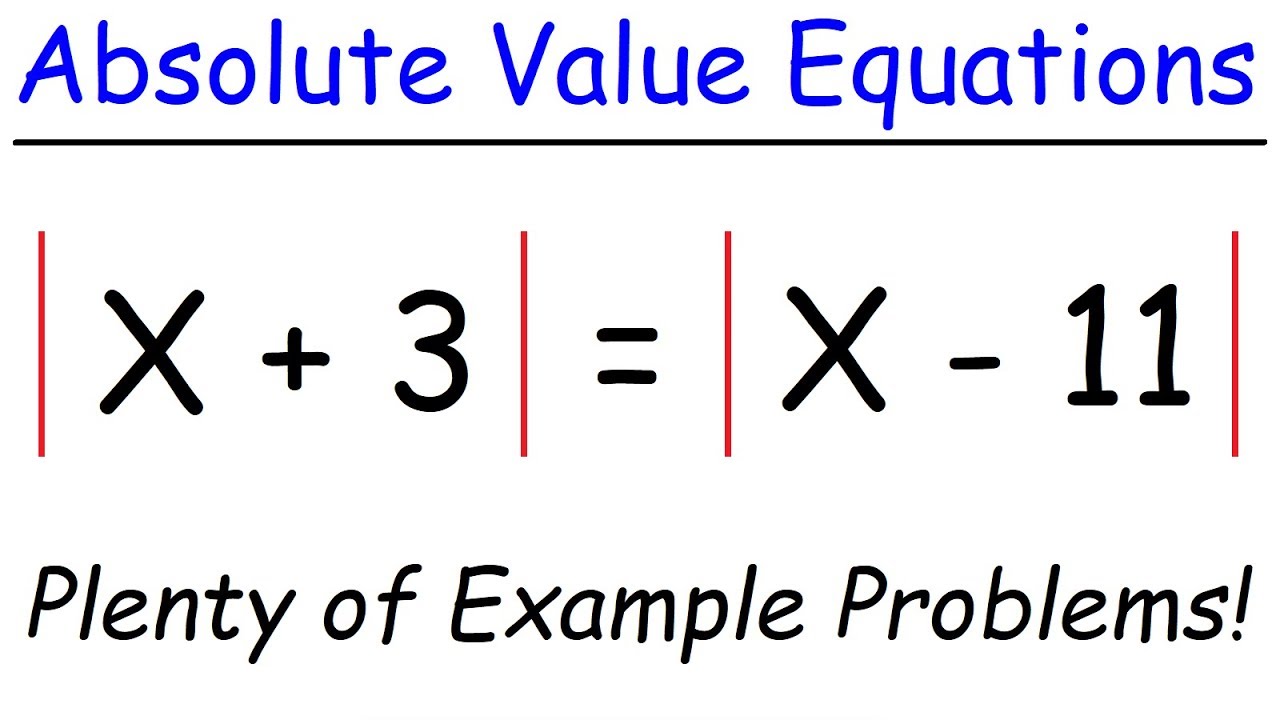Effective Ways to Find Absolute Value
Understanding the Definition of Absolute Value
The **absolute value** of a number represents its distance from zero on a number line, regardless of direction. Mathematically, this means that the **absolute value of negative numbers** is the same as its counterpart as positive. For example, the absolute value of -5 is written as | -5 | = 5, and for +5, | +5 | = 5 as well. The concept of absolute value is fundamental in math, underpinning the **absolute value function** and its significant branches in algebra and calculus. The **definition of absolute value** can be expressed as |x| = x if x ≥ 0 and |x| = -x if x < 0. Understanding this definition helps children grasp its importance regarding **absolute differences** and distance in mathematics.
Visualizing Absolute Values on a Number Line
Visualizing **absolute values in algebra** can be done effectively using a **number line**. This simple representation clarifies how any point on the line corresponds with its absolute value. For instance, if you have the points -3 and 3, both lie three units away from zero; therefore, their absolute values are equal, | -3 | = | 3 | = 3. This visualization assists students with **understanding absolute value** and connects it to the broader topic of **properties of absolute value**, where the recognition that absolute value is always non-negative is reinforced.
Properties and Rules of Absolute Value
There are several essential **properties of absolute value** that are helpful in making calculations efficient. One key property is that |a * b| = |a| * |b|, meaning that the absolute value of the product equals the product of the absolute values. Moreover, for any real numbers a and b, |a – b| indicates the distance between them, which underscores the significance of **absolute value and distance**. Additionally, one must remember that mathematical operations maintain their integrity irrespective of the absolute value in question; thus, managing absolute value equations requires careful application of these key **absolute value rules**.
How to Calculate Absolute Value
So, how do you calculate **absolute value** effectively? Calculating is straightforward once you grasp the rules. If you’re using an **absolute value calculator**, simply input the number, and the tool automatically provides the absolute value. Alternatively, understanding the operations manually stands equally vital. To find the absolute value of negative and positive integers, take the numeric part, conveniently making it a positive if necessary. Moreover, fractions and decimals follow similar rules. For example, the absolute value of -3.14 is | -3.14 | = 3.14, and for fraction -7/2, it would convert to | -7/2 | = 7/2.
Calculating Absolute Value of Fractions and Decimals
When determining **absolute value of fractions**, the approach remains consistent. For instance, let’s say we want to find the **absolute value of fractions** like -3/5. The result will simply render | -3/5 | = 3/5. Similarly, decimals should follow suit. If one wishes to compute the absolute value of negative decimal numbers -2.67, for example, it becomes | -2.67 | = 2.67 when calculated. This helps in comprehending how the concept is consistent across different forms and reinforces mathematical comprehension in students, making the understanding of **absolute value in real numbers** more tangible.
Finding Absolute Value with Examples
Let’s explore a few more examples to solidify our understanding. If we take a negative integer, such as | -8 |, the answer is 8. Similarly, given a very small decimal value such as -0.2, the absolute value again converts it positively yielding | -0.2 | = 0.2. Moreover, seeing how **absolute value examples** apply in regular problems aids in mathematics—like measuring temperatures where -10 degrees would equate to a distance from the neutral point of 10 degrees. Essentially repeating these exercises helps to feel comfortable identifying **absolute value problems** regularly, enhancing proficiency.
Absolute Value in Equations and Inequalities
Working with **absolute value equations** often poses a challenge, but they follow defined paths. For instance, suppose given the equation |x – 3| = 5; this implies two scenarios, where x – 3 can either be 5 or -5. Thus, this breaks down into x – 3 = 5 or x – 3 = -5, leading to solutions x = 8 or x = -2. Practicing such equations provides ample clarity and delves deep into the **absolute value concepts** crucial for advanced mathematics.
Solving Absolute Value Inequalities
When tackling **absolute value inequalities**, the method mirrors a two-sided approach but comes with a slightly nuanced process. For example, for the inequality |x + 1| < 3, we break it into two distinct inequalities, -3 < x + 1 < 3. Thus yielding parallel results -4 < x < 2, which might appear unintuitive but emphasizes the central importance of understanding the graphical representation of these inequalities. Having **absolute value inequalities** opens up perspectives on range and limits, pivotal in advanced mathematical exploration.
Applications of Absolute Value in Everyday Life
Understanding the **absolute value in everyday life** allows students to relate mathematics directly to real-world scenarios. One practical use is in finance, such as determining gains and losses—where finding the actual money lost or spent involves calculating absolute values. Similarly, in geometrical areas, distances measured in absence of directional context signify absolute values—like determining how far out an object is from a central reference point. By recognizing these facets of **absolute value**, learners are better equipped to apply their knowledge beyond the theory.
Absolute Value Tools and Resources for Education
Employing **absolute value tools** besides calculators enhance the learning experience, especially for educators and learners alike. Online **absolute value calculators** can assist students in developing interpretation skills without becoming overwhelmed. Meanwhile, visual tools like graphing calculators represent the **absolute value function graph**, which visually explains how absolute values behave in equations. Starting with resources that furnish numerical **absolute value examples** invigorates the discussion, setting a robust foundation for complex problem-solving later on.
Learning Strategies for Teaching Absolute Value
Different strategies exist for teaching absolute value effectively, paving avenues to diverse learning styles. For instance, grouping students and encouraging collaborative work can demystify equations relating to **absolute value**. Teaching methods integrating visual and interactive tools claim efficacy by fostering a broader understanding beyond mere memorization. Encouraging inquiry-based learning pushes students to explore concepts, creating personal connections to mathematical significance. Furthermore, structured **absolute value exercises** can result in substantial practice oriented around real-world examples.
Common Mistakes with Absolute Value
In this journey of understanding, it’s equally important to highlight **common mistakes with absolute value**. Misinterpreting negative results or overlooking the distance aspect can throw learners off course. Many might confuse the result of equations and fail to evaluate possible branches from one absolute case, yielding incorrect outcomes. Therefore, exercising mindfulness with **absolute value problems** where students evaluate and negotiate challenges leads to significant growth and understanding while bridging gaps left by common errors.
Key Takeaways
- The absolute value reflects the distance of a number from zero, disregarding its sign.
- Calculating absolute values involves transforming negative numbers into positives consistently.
- Absolute value equations and inequalities represent measures that can be tackled through intuitive breakdown methods.
- Real-life applications of absolute value underscore its significance beyond mathematical constructs.
- Employing tools and strategies aids in effectively learning and teaching absolute value.
FAQ
1. What is the absolute value of a complex number?
The **complex absolute value** is determined using the formula |z| = √(a² + b²) where z = a + bi. This depicts the distance of the complex number from the origin in the complex plane. This application connects fundamentally with broader mathematical frameworks.
2. How does absolute value apply in programming?
In programming, the concept of **absolute value in programming** finds applications often in algorithms requiring distance calculations or error evaluations. Many programming languages provide built-in functions (e.g., abs()) to implement absolute value evaluations in calculations seamlessly.
3. What is the significance of absolute value in physics?
In physics, **absolute value** is critical when dealing with quantities such as velocity or acceleration, where direction might be irrelevant, but magnitude is essential. **Absolute value in physics** allows observers to focus purely on these quantities away from directional negotiation.
4. Can you visualize absolute value mathematically with graphs?
The **absolute value graph** is U-shaped centered on the origin, reflecting how absolute values associate with their respective x-values irrespective of their sign. This visualization enhances comprehension of how absolute values reflect properties of functions and domains in mathematics.
5. How does absolute value relate to limits in calculus?
The **relation of absolute value to limits** in calculus is significant when determining approaches to points on the number line. Analyzing limits considers possible discontinuities by evaluating **absolute differences** and behaviors approaching designated points.
6. What are some common terms associated with absolute values?
Terms like **absolute function**, **distance formula**, and **modulus** typically connect to absolute value discussions, augmenting clarity when teaching foundational mathematical concepts that trace back to the logarithmic distance in calculations.
7. How is absolute value helpful in statistics?
In statistics, **absolute value in statistics** is key when determining measures of dispersion or analyzing the error margins between predicted and actual values, reinforcing its importance in statistical evaluations and analyses.