Effective Ways to Explore How Long It Takes to Travel to the Moon in 2025
The journey to the moon has always fascinated humanity, representing both a monumental scientific achievement and an exploration of human potential. If you’re curious about the time to travel to the moon in the context of lunar missions planned for 2025, it’s essential to understand the various factors influencing this duration. From the methods of travel to advancements in space technology, the duration of moon trip can vary significantly. As we look ahead, let’s delve into the anticipated moon trip timeline and what influences travel speed to the moon.
Understanding the Distance to the Moon
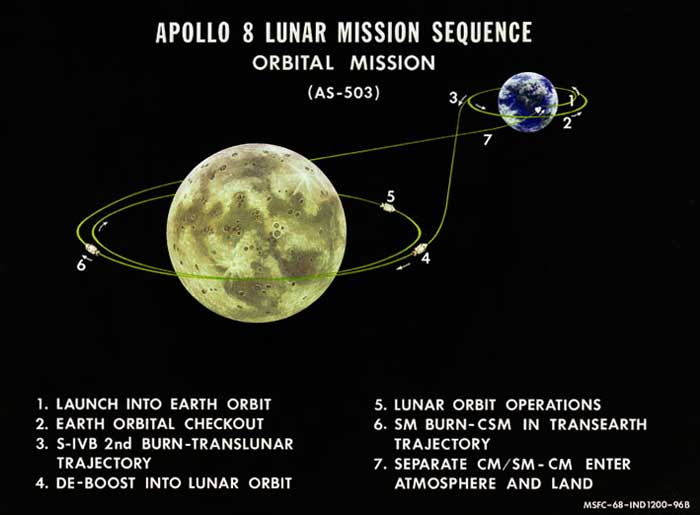
The average distance to the moon is approximately 238,855 miles (384,400 kilometers). This distance can fluctuate slightly due to the moon’s elliptical orbit around the Earth. When discussing the average time to the moon, this vast lunar distance is critical because it directly influences the moon flight time based on the spacecraft’s speed. Historical journeys, like the Apollo mission duration, utilized different travel speeds that significantly impacted the overall mission time. For example, the Apollo 11 mission, which launched in July 1969, took about 76 hours to travel to the moon.
The Impact of Lunar Orbiting Time
The duration of the trip also includes the time spent in lunar orbit before a landing attempt. After reaching the moon, a spacecraft must enter a stable lunar orbit, which could require hours to accomplish before it makes that final descent. The **lunar orbiting time** can be an essential part of the overall journey’s timeline. Each mission’s design will dictate how long it remains in orbit before descending to the lunar surface, affecting the **time taken to reach the moon** from initial launch.
Factors Affecting Travel Speed to the Moon
The speed of travel to the moon varies based on spacecraft propulsion technology and mission design. Traditional rockets have achieved speeds above 3,500 miles per hour for lunar transit, but newer technologies are being developed. Understanding the **travel speed to the moon** entails examining different spacecraft prototypes that may be faster, alongside analyzing projected technological advancements in **lunar travel technologies**. As we assess future options, this exploration will be paramount to improve the **anticipated moon trip duration**.
Current Spacecraft and Their Moon Travel Logistics
As we prepare for upcoming lunar missions, it’s crucial to consider how various spacecraft will handle the moon travel logistics. NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft are designed for manned missions but have different capabilities and **mission schedules**. Understanding these logistics will highlight how current missions differ from previous Apollo missions, influencing both **moon exploration time frame** and **manned mission to the moon** goals for coming years.
Comparing Spacecraft for Optimal Travel Methods
When discussing **travel methods to the moon**, comparing spacecraft, such as those crafted by SpaceX, Blue Origin, and NASA, reveals exciting possibilities. For example, SpaceX has plans for reusable rockets which could drastically cut down on costs and time for **space shuttle moon journeys**. Studying these current missions can provide insights into potential enhancements in transport efficiency, and potentially alter the **journey to the moon duration**, ensuring we’re equipped with innovative solutions.
Challenges in Moon Travel Preparations
With all advancements, potential challenges still persist, ranging from navigation difficulties to radiation exposure concerns. The **time frame for moon mission** readiness includes rigorous training for astronauts and ensuring the baggage requirements for a **moon travel itinerary** are met. This also encompasses **lunar trip requirements** to safeguard human life, which are crucial for achieving safe and stable missions historically viable across time.
The Future of Moon Expeditions in 2025
As we approach 2025, the landscape of lunar exploration is set for a dramatic shift. The integration of commercial entities in **future moon travel estimates** indicates a blossoming opportunity for **moon tourism**. With planned runs by companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin, we anticipate a more frequent and cost-effective approach to lunar exploration, drastically changing **moon expedition timing** in years to come. Commercial and national agencies are poised to work synchronously towards a regular appointed schedule for lunar missions, influencing not just commercial travel but scientific advancements as well.
Advancements in Travel Technology
In reviewing the **evolving moon travel technologies**, innovations in spacecraft materials, fuels, and life support systems will likely lead to reduced costs and decrease travel times. Technologies revolving around rapid propulsion, such as ion thrusters or nuclear thermal propulsion, may redefine our possibilities for **human travel to the moon**, and it warrants necessary investment in research. Enhanced understanding of **weightlessness effects** and **human adaptability to space** will also promote safer and longer trips without adverse effects on astronaut health.
Living and Working on the Moon
Moreover, the timeline of establishing human habitats on the moon directly affects **moon travel experiences**. Early deployments might begin with unmanned vehicles to setup infrastructure and support for **human settlements on the moon**, which will expand the opportunities for ongoing lunar trips in the **future of lunar tourism**. The **planning moon expeditions** needs focus on sustainable practices; ushering in an era of ecological balance within space travel as part of our exploration drive.
Key Takeaways
- The average travel time to the moon varies from 72 to 84 hours depending on the spacecraft’s technology.
- Future lunar missions are gearing toward collaborative efforts involving private companies to improve efficiency and accessibility.
- Ongoing advancements in planning and preparing for moon expeditions promise exciting developments for lunar travel timelines.
- Understanding moon travel logistics and technological innovations is crucial for successful future moon missions.
- Commercial interest is shaping the future of lunar tourism, potentially allowing more people to experience the moon than ever before.
FAQ
1. What is the typical time taken to reach the moon?
The typical travel time to the moon during past missions has ranged from about 72 to 84 hours, depending on various factors such as spacecraft speed and mission specifics. Future advancements could further optimize this timeline.
2. What factors influence the duration of a lunar trip?
Several factors affect the **duration of moon trip**, including the spacecraft’s speed, trajectory, launch window, and orbiting requirements once reaching the lunar vicinity. Innovations in propulsion technology are also expected to play a significant role.
3. How has the Apollo mission duration compared to modern plans?
The Apollo missions took about three days for travel to the moon. In contrast, modern spacecraft designs and private flights may offer similar duration but utilize improved technology that could change operational efficiency, aiming for quicker travel times.
4. Are there plans for commercial moon travel?
Yes, multiple companies are preparing for **commercial moon travel**, with initiatives focused on developing reusable rockets and innovative lunar landers that prioritize safety and cost-effectiveness, thereby making trip possibilities accessible to the general public.
5. How will technology impact the speed of travel to the moon?
Advancements in propulsion technology, such as ion thrusters or nuclear propulsion systems, could significantly enhance the speed of travel to the moon. Evaluating fuel efficiency and trajectories will become more sophisticated, shortening mission durations further.